High blood sugar levels are dangerous for your health. High blood sugar may lead to a plethora of undesirable health complications. Controlling and preventing high blood sugar levels may be accomplished by various means.
The majority of people probably do not get enough exercise. With our hectic schedules and Netflix marathons, we’re fortunate to break a sweat before sleep. However, the local park walk you take in the afternoon is beneficial for more than simply your health.
Ever wonder about what to do when blood sugar is high? How to reduce blood sugar level immediately? What level of blood sugar is dangerous for type 2 diabetes? Is blood sugar level of 400 dangerous? What if my blood sugar level is 17? Check out this article for informative insights!
Table of Contents
Blood sugar is dangerous

Having diabetes means that your blood glucose levels are unhealthily high. The eyes, kidneys, and nerves may all suffer harm when blood sugar levels are too high. Additionally, it has been linked to heart disease and stroke.
Keeping your blood sugar under control with insulin is the only method to avoid developing this condition.
Normal blood sugar levels
Normal blood sugar levels are between 70 and 100 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL). This indicates that the typical blood sugar level is between 100 and 150 mg/dL.
Normal blood glucose levels are essential for the correct functioning of the body. If your blood glucose levels are too high, you may develop type 2 diabetes, which may cause long-term harm to your health.
Simply put, diabetes is characterized by a high blood glucose level. A routine of testing and level management accompanies the condition.
However, “normal” levels of blood glucose should be maintained, regardless of the type of diabetes. Here, we examine these values and normal blood glucose levels for those without diabetes.
High blood sugar levels
Hyperglycemia is a disorder that affects the quantity of sugar in the blood. When blood glucose levels are high, the body may be unable to use insulin effectively.
High glucose levels arise when the body lacks sufficient insulin or cannot utilize the insulin it has effectively to transport glucose from circulation to the body’s muscles, organs, and tissues for energy—consequently, the quantity of sugar in the blood increases.
Hyperglycemia often occurs when you eat more carbs or more significant amounts of food than usual, when you do not take enough insulin or other diabetic medicine as recommended, and when you reduce your physical activity levels. Additionally, elevated amounts of stress might raise blood sugar levels. Steroids, beta-blockers, birth control pills, and numerous mental health treatments are among the non-diabetes-related medications known to increase blood sugar levels.
Signs of high blood sugar include frequent urination, weariness, dry or itchy skin, thirst, an increase in the frequency of infections, and eating more but not gaining as much weight as normal.
Low Blood Sugar
Low blood sugar occurs when insufficient glucose is in circulation to continue giving energy to the organs, muscles, and tissues. Given your blood-sugar-lowering drugs and amount of physical activity, it happens most often when you don’t consume enough meals, particularly carb-containing foods. Levels might fall gradually or abruptly.
When the glucose level in the circulation falls too low, the body releases epinephrine, often known as adrenaline or the “fight or flight” hormone. Epinephrine increases the heart rate and may produce sweat, trembling, anxiety, and irritation. Concentration issues, mental confusion, and slurred speech may occur if insufficient glucose reaches the brain. A shortage of glucose in the brain may cause convulsions, coma, and even death in severe circumstances.
People with low blood glucose (below 70 mg/dL) may apply the ADA’s “15-15 Rule,” which instructs them to ingest 15 g of carbohydrates, wait 15 minutes, and then recheck their glucose levels. If the figure remains low, continue until it reaches at least 70 mg/dL.
Symptoms of high blood sugar

People who have diabetes often experience a gradual onset of the symptoms of hyperglycemia over a few days or weeks. There may be no symptoms until the blood glucose level has reached a very high level in certain circumstances.
The following are some of the symptoms of hyperglycemia:
- increased thirst as well as a dry mouth
- the urgent desire to urinate more often
- tiredness
- the vision that is not clear
- loss of weight for no apparent reason
- illnesses that come back often, such as thrush, cystitis, and skin infections
If you have symptoms of hyperglycemia and are concerned that you could have undetected diabetes, make an appointment with your primary care physician.
What is blood sugar chart?
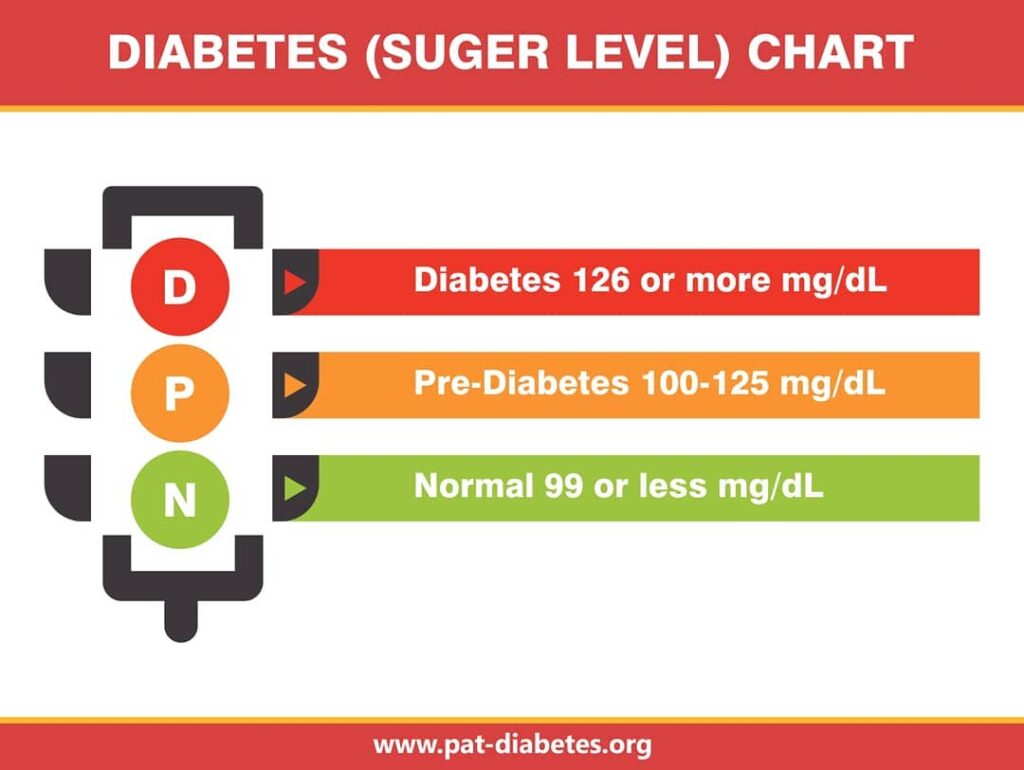
If you have diabetes, the therapy you get will be successful based on how well you manage to keep your blood sugar under control. It is possible to enhance both short-term and long-term health outcomes with effective self-management. If you have just been diagnosed with diabetes, use the”Blood Sugar Calculator” tool and the information it provides.
You will be better able to educate yourself and take control of your health by using it. You will eventually acquire the knowledge necessary to self-manage the disease and will get an understanding of the reasons behind the fluctuations in your sugar level.
The blood sugar chart includes explanations of blood sugar results in terms of milligrams per deciliter (mg/dl) based on the kind of test – fasting sugar, after-meal or post-prandial, and glucose tolerance test (GTT) for a normal individual, in early diabetes, and in established diabetes.
FAQs
At what level is blood sugar dangerous?
Excessively high or low blood sugar levels might be harmful. Normal blood glucose levels vary between 70 and 100 milligrams per deciliter. Hypoglycemia is diagnosed when blood sugar levels fall below 70 milligrams per deciliter. Hypoglycemia may lead to seizures, coma, or death if left untreated.
What causes blood sugar to be high?
There are a variety of variables that might contribute to elevated blood sugar levels. The most prevalent cause is excessive sugar consumption. Additionally, if you haven’t eaten enough in the last several hours, your body may attempt to compensate by breaking down more food than normal.
Diabetes, which occurs when the body cannot metabolize glucose efficiently, may influence your blood sugar and insulin levels.
What are blood sugar targets?
The blood sugar target is the amount of blood sugar (glucose) you want to maintain throughout the day. Normal blood glucose levels vary from 70 to 100 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL). Maintaining blood sugar levels as near to normal as feasible is the objective.
Conclusion
Since blood sugar is such a complex problem for most individuals, it is essential to adopt measures to reduce your risk and manage the symptoms. Only some people can adequately control their blood sugar via food alone. In addition to supplements like oregano oil, cinnamon, and butter oil, you may take several more measures to lower your blood sugar.
Depending on your circumstances, more than this may be required. In the event of more severe blood sugar issues like diabetes, you may also need expert assistance. However, remember that a healthy lifestyle, including correct nutrition and exercise, will greatly regulate your blood sugar.

